Secure Act 2.0 (Retirement/Educational Loans)
- Secure Act 2.0 - (Retirement/Educational Loans)
December 12, 2024
12:00 pm - 1:30 pm
This meeting will be *VIRTUAL*
Business Meeting- 12:30pm to 1:30pm
Secure Act 2.0 – (Retirement/Educational Loans) – Presented by: Michael Abbate – ATLAS CPA’s & Advisors PLLC
Effectively saving for retirement has been a longstanding (and growing) issue nationwide, but student loan matching offers a method of solving two problems at the same time.
With student loan matching, companies can contribute to your retirement savings so you still receive the ever-so-important compounding effect while also being able to pay down your student loan debt.
Another way to consider it– the government is putting a much-needed incentive in place that helps student loan borrowers pay down debt faster.
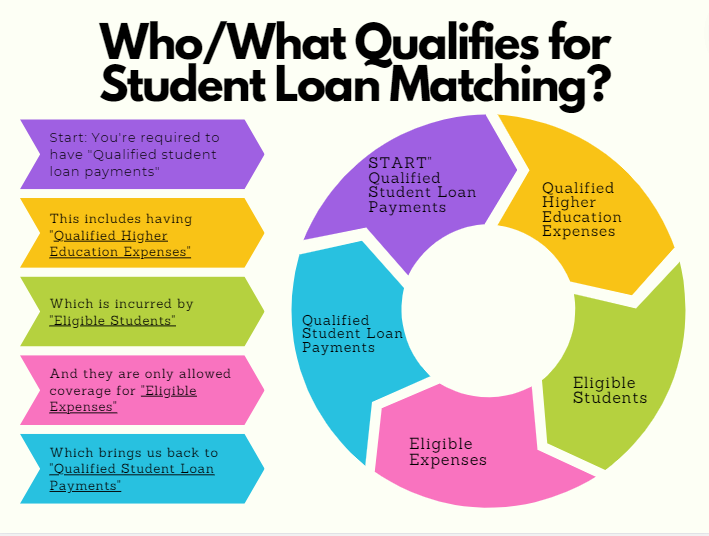
Who Qualifies for student loan matching?
The beneficiary of the student loan is qualified to receive student loan matching from their employer. The details are both vague and intricate but here’s what we know for sure based on the official SECURE 2.0 Act document.
The flow is a bit obscure (as is tax code with the IRS), so here’s a graphic to break it down followed by the text to further explain the web of requirements in detail:
The official text reads “Section 110 permits an employer to make matching contributions under a 401(k) plan, 403(b) plan, or SIMPLE IRA with respect to “qualified student loan payments.”
- “Qualified student loan payments” are defined by the IRS as a loan taken out for the sole purpose of paying for a qualified higher education expense for:
– You, your spouse or your dependent when you took out the loan
– Education during an academic period for an eligible student and paid (received) within a reasonable period time before or after you took the loan out. - “Qualified higher education expenses” are defined by the IRS as tuition, fees or other related expenses for an eligible student.
- “Eligible student” is defined by the IRS as an individual who is enrolled at least half-time (6 credits) in a program of study leading to a degree, certificate, or other recognized educational credential at an eligible educational institution.
- “Eligible expenses” are defined by the IRS as required student activity fees, books or anything that is required to enroll or attend the school.
Venue: Virtual Meeting